A Beginner's Guide to Datasets for AI Model Training
In the world of artificial intelligence (AI), datasets are the building blocks upon which models are trained to perform various tasks like image recognition, natural language processing, and predictive analytics. Whether you're just dipping your toes into the vast ocean of AI or you're a seasoned data scientist, understanding datasets is crucial.
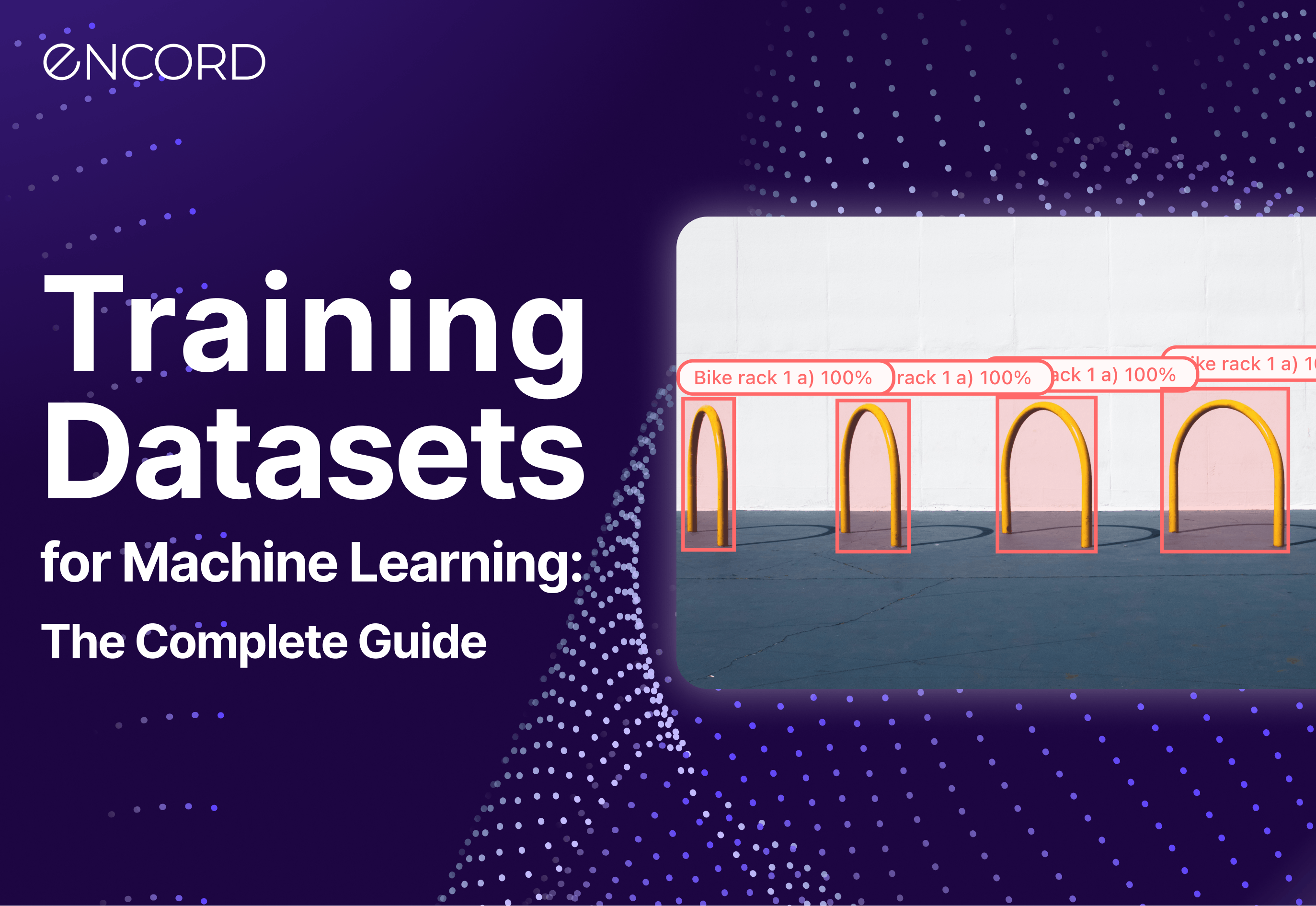
What are Datasets?
Datasets are collections of structured or unstructured data that are used to train, validate, and test AI models. These data can come in various formats, including spreadsheets, text files, images, videos, and more. Datasets serve as the foundation for teaching AI algorithms to recognize patterns, make predictions, or understand natural language.
Types of Datasets
1. Structured Datasets: These datasets have a well-defined format with organized rows and columns, often resembling tables. Examples include CSV files, databases, and spreadsheets containing numerical or categorical data.
2. Unstructured Datasets: Unlike structured datasets, unstructured datasets lack a predefined format and organization. Examples include images, audio recordings, text documents, and videos.
3. Semi-Structured Datasets: These datasets have some structure but may also contain unstructured elements. Examples include JSON and XML files, which have a defined structure but may include free-form text or nested data.
Where to Find Datasets?
1. Public Datasets: Many organizations, research institutions, and government agencies release datasets for public use. Platforms like Kaggle, UCI Machine Learning Repository, and Google Dataset Search are popular sources for finding diverse datasets across various domains.
2. Commercial Datasets: Some datasets are available for purchase from specialized data providers like ADA Data Collection, FactSet Data. These datasets may offer unique insights or specialized data that are not freely available.
3. Creating Your Own Datasets: In some cases, you may need to collect and label your own data to suit your specific AI project with the help of platforms like Roboflow. This process involves data gathering, preprocessing, and annotation, which can be time-consuming but is often necessary for custom applications.
Tips for Using Datasets Effectively
1. Understand Your Problem: Before selecting a dataset, clearly define the problem you want to solve and the type of data required to address it. Choose a dataset that aligns with your project goals and requirements.
2. Explore and Preprocess the Data: Thoroughly explore the dataset to understand its structure, quality, and potential biases. Preprocess the data by cleaning, normalizing, and transforming it to prepare it for model training.
3. Split the Data: Divide the dataset into training, validation, and testing sets to evaluate the performance of your AI model accurately. Typically, the training set is used to train the model, the validation set is used to tune hyperparameters, and the testing set is used to assess the model's performance.
4. Consider Data Augmentation: For image and text data, consider applying data augmentation techniques to increase the diversity of your dataset and improve model generalization.
5. Handle Imbalanced Data: If your dataset contains imbalanced classes, employ techniques like oversampling, undersampling, or class weighting to ensure that the model learns from all classes equally.
Conclusion
In the realm of AI, datasets play a pivotal role in training robust and accurate models. By understanding the types of datasets available, where to find them, and how to use them effectively, you can embark on your AI journey with confidence. Whether you're a beginner or an experienced practitioner, mastering the art of dataset selection and utilization is essential for building successful AI applications.
What's Your Reaction?